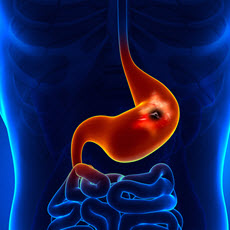
A peptic ulcer is a sore in the lining of your stomach or your duodenum, the first part of your small intestine. A burning stomach pain is the most common symptom. The pain:
- Starts between meals or during the night
- Briefly stops if you eat or take antacids
- Lasts for minutes to hours
- Comes and goes for several days or weeks
Peptic ulcers happen when the acids that help you digest food damage the walls of the stomach or duodenum. The most common cause is infection with a bacterium called Helicobacter pylori. Another cause is the long-term use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs) such as aspirin and ibuprofen. Stress and spicy foods do not cause ulcers, but can make them worse.
- Peptic Ulcer (National Library of Medicine)A peptic ulcer is a sore in the lining of your stomach or your duodenum, the first part of your ...
- A peptic ulcer is an open sore or raw area in the lining of the stomach or intestine. There are two types of peptic ulcers: Gastric ...
- ... ulcer) or upper part of the small intestine (duodenal ulcer). This article describes how to care for yourself ... You have peptic ulcer disease (PUD). You may have had tests to help diagnose your ulcer. One of these tests may have ...
- Definition & Facts for Peptic Ulcers (Stomach or Duodenal Ulcers)
 (National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases) Overview of peptic (stomach or duodenal) ulcers, sores on the lining of the stomach or duodenum that can lead to complications such as bleeding or perforation.
(National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases) Overview of peptic (stomach or duodenal) ulcers, sores on the lining of the stomach or duodenum that can lead to complications such as bleeding or perforation. - Diagnosis of Peptic Ulcers (Stomach or Duodenal Ulcers)
 (National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases) Peptic ulcer diagnosis, stomach ulcer diagnosis, duodenal ulcer diagnosis, Helicobacter pylori, H. pylori, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, NSAIDs, blood test, stool test, urea breath test, upper GI endoscopy, upper GI ...
(National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases) Peptic ulcer diagnosis, stomach ulcer diagnosis, duodenal ulcer diagnosis, Helicobacter pylori, H. pylori, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, NSAIDs, blood test, stool test, urea breath test, upper GI endoscopy, upper GI ... - Peptic Ulcer/Clinical Trials ... Peptic Ulcer
- Treatment for Peptic Ulcers (Stomach Ulcers)
 (National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases) Learn about peptic (stomach or duodenal) ulcer treatment, such as PPIs to heal ulcers, medicines to treat H. pylori, and medicine changes to treat NSAID ulcers.
(National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases) Learn about peptic (stomach or duodenal) ulcer treatment, such as PPIs to heal ulcers, medicines to treat H. pylori, and medicine changes to treat NSAID ulcers. - Symptoms and Causes of Peptic Ulcer Disease
 (National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases) Learn about symptoms of peptic (stomach or duodenal) ulcers, such as abdominal pain, nausea, bloating, and belching. H. pylori and NSAIDs are common causes.
(National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases) Learn about symptoms of peptic (stomach or duodenal) ulcers, such as abdominal pain, nausea, bloating, and belching. H. pylori and NSAIDs are common causes. - ... bacteria (germ) responsible for most stomach (gastric) and duodenal ulcers and many cases of stomach inflammation (chronic gastritis ).
- Helicobacter Pylori Infections (National Library of Medicine)... the stomach. It is the main cause of peptic ulcers, and it can also cause gastritis and stomach ... inflammation. This can lead to gastritis or a peptic ulcer. Researchers aren't sure how H. pylori spreads. ...



